学习任务
线程的创建和取消
线程的参数传递
线程资源的回收,让线程有计划的退出
线程的取消
线程和信号,与多进程的信号有不同
线程安全,一切麻烦从共享资源开始
线程同步,各种锁的使用
生产者消费者模型,代码
开发多进程网路服务程序
进程和线程的区别
- 进程优点:可以在一个进程内是实现并发。
- 开销小创建线程比创建进程要快。
- 进程有pcb,有独立地址空间,线程本质还是进程, 线程有pcn没有独立地址空间
- 多进程,子进程挂了不影响其他进程。 多线程,一个子线程挂了,整个进程玩完犊子。
线程的创建和终止
创建,等待线程退出,查看线程
创建线程
int pthread_create(pthread_t *thread, const pthread_attr_t *attr,void *(*start_routine) (void *), void *arg);
等待线程退出 pthread_join(id,退出返回值);
查看线程 ps- Lf 线程编号
代码如下:
#include <pthread.h>
void* arg_main1(void* arg) {
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) {
printf("thread 1 sleep %d\n",i);
}
}
void* arg_main2(void* arg) {
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) {
printf("thread2 sleep %d\n",i);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t pid1,pid2;
int arg = 4;
if( pthread_create(&pid1,NULL,&arg_main1,(void*)&arg) != 0) {
perror("pthread_create2 failed \n");
return -1;
}
if( pthread_create(&pid2,NULL,&arg_main2,(void*)&arg) != 0) {
perror("pthread_create2 failed \n");
return -1;
}
sleep(70);
// 等待线程退出
pthread_join(pid1,NULL);
pthread_join(pid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
线程非正常终止
- 主线程退出,全部线程将强行终止。 所以多线程程序主线程是不能退出的。
- 在子线程中调调用exit() 函数会终止整个进程。(如果是多进程,子进程退出后,其他进程会继续运行。)
a. return 和 exit() 的区别. return 会返回主线程。 exit()线程直接退出 - 给多线程发信号缺省是终止整个进程。
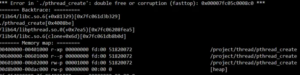
- 在多线程程序中,某一个子线程coredump了,整个进程异常退出。
线程coredump整个进程异常退出
void* arg_main2(void* arg) {
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
// int* a= new int(23);
// delete a;
// delete a;
for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) {
printf("thread2 sleep %d\n",i);
}
}
终止线程的三种方法
- return 和pthread_exit() 的区别?
a. return 回到线程主函数。不能终止
b. pthread_exit() 会终止线程。 - 线程可以从线程函数中返回,返回值是线程的退出码。
- 线程可以被同一进程中其他线程调用pthread_cancel() 取消。
4.在线程函数中调用pthread_exit() 退出
线程的参数传递
- 创建线程不会保证那个线程的执行顺序
- 不能用全局变量代替线程函数的参数。
- 数据类型的强制转换。
- 如何传递地址参数。
- 传递地址参数。
- 线程退出状态。
数据类型的强制转换。
int ii = 10;
void *pv = NULL;
pv = (void*)(long)ii;
printf("pv = %p \n",pv);
int jj = 0;
jj = (int)(long)pv;
printf("jj = %d \n",jj);
![]()
具体使用:
void* arg_main1(void* arg) {
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) {
printf("thread 1 sleep %d\n",i);
if(i == 2) func2();
}
}
void* arg_main2(void* arg) {
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
// int* a= new int(23);
// delete a;
// delete a;
for(int i = 0;i < cnt; i++) {
printf("thread2 sleep %d\n",i);
if(i == 2) func();
}
}
void func() {
pthread_exit(0);
}
void func2() {
return ;
}
int main()
{
////////////////////////////////////////////
pthread_t pid1,pid2;
int arg = 4;
pthread_create(&pid1,NULL,&arg_main1,(void*)(long)&arg) != 0);
arg = 7;
pthread_create(&pid2,NULL,&arg_main2,(void*)(long)&arg) != 0);
/////////////////////////////////
// 等待线程退出
pthread_join(pid1,NULL);
pthread_join(pid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
线程传递地址参数。(把结构体的地址传递给线程函数使用)
struct stu {
int age;
char name[21];
};
void* arg_main1(void* arg) {
struct stu *p = (struct stu*)arg;
printf("age = %d \n",p->age);
delete p;
}
void* arg_main2(void* arg) {
struct stu *p = (struct stu*)arg;
printf("age = %d \n",p->age);
delete p;
}
int main()
{
////////////////////////////////////////////
struct stu *student = new struct stu;
student->age = 98;
strcpy(student->name,"yazh");
pthread_t pid1,pid2;
int arg = 4;
pthread_create(&pid1,NULL,&arg_main1,(void*)student);
struct stu *student2 = new struct stu;
student2->age = 928;
strcpy(student2->name,"yazh2");
pthread_create(&pid2,NULL,&arg_main2,(void*)student2);
/////////////////////////////////
// 等待线程退出
pthread_join(pid1,NULL);
pthread_join(pid2,NULL);
return 0;
}
使用2
/ 本程序演示线程参数的传递(用结构体的地址传递多个参数)。
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pthread.h>
void *thmain(void *arg); // 线程的主函数。
struct st_args
{
int no; // 线程编号。
char name[51]; // 线程名。
};
int main(int argc,char *argv[])
{
pthread_t thid=0;
// 创建线程。
struct st_args *stargs=new struct st_args;
stargs->no=15; strcpy(stargs->name,"测试线程");
if (pthread_create(&thid,NULL,thmain,stargs)!=0) { printf("pthread_create failed.\n"); exit(-1); }
// 等待子线程退出。
printf("join...\n");
pthread_join(thid,NULL);
printf("join ok.\n");
}
void *thmain(void *arg) // 线程主函数。
{
struct st_args *pst=(struct st_args *)arg;
printf("no=%d,name=%s\n",pst->no,pst->name);
delete pst;
printf("线程开始运行。\n");
}
线程退出 pthread_join
进程和线程的退出状态并不关心。pthread_join 可以拿到返回值,
进程使用wait
#include <stdio.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <malloc.h>
#include <string.h>
void* arg_main(void* arg);
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) {
pthread_t pid;
int thread_param = 4;
if (pthread_create(&pid,NULL,&arg_main,(void*)&thread_param) !=0) {
printf("pthread_create failed \n");
return -1;
}
// 等待线程的退出。
void* ret;
if (pthread_join(pid,&ret) != 0) {
printf("pthread_join failed \n");
return -1;
}
if(ret != NULL) {
printf("msg = %s \n",ret);
}
puts("end of main() \n");
free(ret);
}
void* arg_main(void* arg) {
int i;
int cnt = *((int*)arg);
char* msg = (char*)malloc(sizeof(char) * 50);
strcpy(msg,"hello i am thread\n");
for(i = 0;i < cnt ;i++) {
sleep(1);
printf("pthread running \n");
}
return (void*)msg;
}