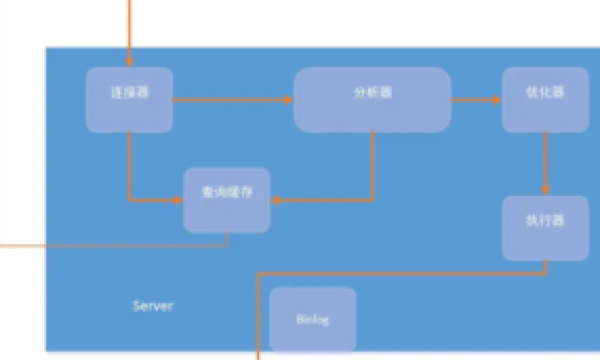
DDL—数据定义语言(Create,Alter,Drop,DECLARE)
DML—数据操纵语言(Select,Delete,Update,Insert)
DCL—数据控制语言(GRANT,REVOKE,COMMIT,ROLLBACK)
首先,简要介绍基础语句:
1、说明:创建数据库
Create DATABASE database-name
2、说明:删除数据库
drop database dbname
3、说明:备份sql server
--- 创建 备份数据的 device USE master EXEC sp_addumpdevice 'disk', 'testBack', 'c:\mssql7backup\MyNwind_1.dat' --- 开始 备份 BACKUP DATABASE pubs TO testBack
4、说明:创建新表
create table tabname(col1 type1 [not null] [primary key],col2 type2 [not null],..)
根据已有的表创建新表:
A:create table tab_new like tab_old (使用旧表创建新表) B:create table tab_new as select col1,col2… from tab_old definition only
5、说明:删除新表
drop table tabname
6、说明:增加一个列
Alter table tabname add column col type
注:列增加后将不能删除。DB2中列加上后数据类型也不能改变,唯一能改变的是增加varchar类型
的长度。
7、
说明:添加主键: Alter table tabname add primary key(col) 说明:删除主键: Alter table tabname drop primary key(col)
8、说明:
创建索引:create [unique] index idxname on tabname(col….) 删除索引:drop index idxname
注:索引是不可更改的,想更改必须删除重新建。
9、说明:创建视图:
create view viewname as select statement 删除视图:drop view viewname
10、说明:几个简单的基本的sql语句
选择:select * from table1 where 范围 插入:insert into table1(field1,field2) values(value1,value2) 删除:delete from table1 where 范围 更新:update table1 set field1=value1 where 范围 查找:select * from table1 where field1 like '%value1%' ---like的语法很精妙,查资料! 排序:select * from table1 order by field1,field2 [desc] 总数:select count as totalcount from table1 求和:select sum(field1) as sumvalue from table1 平均:select avg(field1) as avgvalue from table1 最大:select max(field1) as maxvalue from table1 最小:select min(field1) as minvalue from table1
11、说明:几个高级查询运算词
A: UNION 运算符
UNION 运算符通过组合其他两个结果表(例如 TABLE1 和 TABLE2)并消去表中任何重复行而派生 出一个结果表。当 ALL 随 UNION 一起使用时(即 UNION ALL),不消除重复行。两种情况下,派 生表的每一行不是来自 TABLE1 就是来自 TABLE2。
B: EXCEPT 运算符
EXCEPT 运算符通过包括所有在 TABLE1 中但不在 TABLE2 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个 结果表。当 ALL 随 EXCEPT 一起使用时 (EXCEPT ALL),不消除重复行。
C: INTERSECT 运算符
INTERSECT 运算符通过只包括 TABLE1 和 TABLE2 中都有的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个结果 表。当 ALL 随 INTERSECT 一起使用时 (INTERSECT ALL),不消除重复行。 注:使用运算词的几个查询结果行必须是一致的。
12、说明:使用外连接
A、left outer join:
左外连接(左连接):结果集几包括连接表的匹配行,也包括左连接表的所有行。 sql: select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c
B:right outer join:
右外连接(右连接):结果集既包括连接表的匹配连接行,也包括右连接表的所有行。
C:full outer join:
全外连接:不仅包括符号连接表的匹配行,还包括两个连接表中的所有记录。
13、说明:复制表(只复制结构,源表名:a 新表名:b) (Access可用)
法一:select * into b from a where 1<>1
法二:select top 0 * into b from a
14、说明:拷贝表(拷贝数据,源表名:a 目标表名:b) (Access可用)
insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b;
15、说明:跨数据库之间表的拷贝(具体数据使用绝对路径) (Access可用)
insert into b(a, b, c) select d,e,f from b in ‘具体数据库' where 条件
例子:..from b in ‘”&Server.MapPath(“.”)&”\data.mdb” &”‘ where..
16、说明:子查询(表名1:a 表名2:b)
select a,b,c from a where a IN (select d from b ) 或者: select a,b,c from a where a IN (1,2,3)
17、说明:显示文章、提交人和最后回复时间
select a.title,a.username,b.adddate from table a,(select max(adddate) adddate from table where table.title=a.title) b
18.说明:外连接查询(表名1:a 表名2:b)
select a.a, a.b, a.c, b.c, b.d, b.f from a LEFT OUT JOIN b ON a.a = b.c
19、说明:在线视图查询(表名1:a )
select * from (Select a,b,c FROM a) T where t.a > 1;
20、说明:between的用法,between限制查询数据范围时包括了边界值,not between不包括
select * from table1 where time between time1 and time2 select a,b,c, from table1 where a not between 数值1 and 数值2
21、说明:in 的使用方法
select * from table1 where a [not] in (‘值1','值2','值4','值6')
22、说明:两张关联表,删除主表中已经在副表中没有的信息
delete from table1 where not exists ( select * from table2 where table1.field1=table2.field1 )
23、说明:四表联查问题:
select * from a left inner join b on a.a=b.b right inner join c on a.a=c.c inner join d on a.a=d.d where .....
24、说明:日程安排提前五分钟提醒
sql: select * from 日程安排 where datediff('minute',f开始时间,getdate())>5
25、说明:一条sql 语句搞定数据库分页
select top 10 b.* from (select top 20 主键字段,排序字段 from 表名 order by 排序字段 desc) a,表名 b where b.主键字段 = a.主键字段 order by a.排序字段
26、说明:前10条记录
select top 10 * form table1 where 范围
27、说明:选择在每一组b值相同的数据中对应的a最大的记录的所有信息(类似这样的用法可以用
于论坛每月排行榜,每月热销产品分析,按科目成绩排名,等等.)
select a,b,c from tablename ta where a=(select max(a) from tablename tb where tb.b=ta.b)
28、说明:包括所有在 TableA 中但不在 TableB和TableC 中的行并消除所有重复行而派生出一个
结果表
(select a from tableA ) except (select a from tableB) except (select a from tableC)
29、说明:随机取出10条数据
select top 10 * from tablename order by newid()
30、说明:随机选择记录
select newid()
31、说明:删除重复记录
Delete from tablename where id not in (select max(id) from tablename group by col1,col2,...)
32、说明:列出数据库里所有的表名
select name from sysobjects where type='U'
33、说明:列出表里的所有的
select name from syscolumns where id=object_id('TableName')
34、说明:列示type、vender、pcs字段,以type字段排列,case可以方便地实现多重选择,类似
select 中的case。
select type,sum(case vender when 'A' then pcs else 0 end),sum(case vender when 'C' then pcs else 0 end),sum(case vender when 'B' then pcs else 0 end) FROM tablename group by type
显示结果:
type vender pcs
电脑 A 1
电脑 A 1
光盘 B 2
光盘 A 2
手机 B 3
手机 C 3
35、说明:初始化表table1
TRUNCATE TABLE table1
36、说明:选择从10到15的记录
select top 5 * from (select top 15 * from table order by id asc) table_别名 order by id desc
随机选择数据库记录的方法(使用Randomize函数,通过SQL语句实现)
对存储在数据库中的数据来说,随机数特性能给出上面的效果,但它们可能太慢了些。你不能
要求ASP“找个随机数”然后打印出来。实际上常见的解决方案是建立如下所示的循环:
Randomize
RNumber = Int(Rnd*499) +1
While Not objRec.EOF
If objRec("ID") = RNumber THEN
... 这里是执行脚本 ...
end if
objRec.MoveNext
Wend
这很容易理解。首先,你取出1到500范围之内的一个随机数(假设500就是数据库内记录的总
数)。然后,你遍历每一记录来测试ID 的值、检查其是否匹配RNumber。满足条件的话就执行由
THEN 关键字开始的那一块代码。假如你的RNumber 等于495,那么要循环一遍数据库花的时间可就
长了。虽然500这个数字看起来大了些,但相比更为稳固的企业解决方案这还是个小型数据库了,
后者通常在一个数据库内就包含了成千上万条记录。这时候不就死定了?
采用SQL,你就可以很快地找出准确的记录并且打开一个只包含该记录的recordset,如下所示
:
Randomize
RNumber = Int(Rnd*499) + 1
sql = "Select * FROM Customers Where ID = " & RNumber
set objRec = ObjConn.Execute(SQL)
Response.WriteRNumber & " = " & objRec("ID") & " " & objRec("c_email")
不必写出RNumber 和ID,你只需要检查匹配情况即可。只要你对以上代码的工作满意,你自可
按需操作“随机”记录。Recordset没有包含其他内容,因此你很快就能找到你需要的记录这样就
大大降低了处理时间。
再谈随机数
现在你下定决心要榨干Random 函数的最后一滴油,那么你可能会一次取出多条随机记录或者
想采用一定随机范围内的记录。把上面的标准Random 示例扩展一下就可以用SQL应对上面两种情况
了。
为了取出几条随机选择的记录并存放在同一recordset内,你可以存储三个随机数,然后查询
数据库获得匹配这些数字的记录:
sql = "Select * FROM Customers Where ID = " & RNumber & " or ID = " & RNumber2 & " or ID = " & RNumber3
假如你想选出10条记录(也许是每次页面装载时的10条链接的列表),你可以用BETWEEN 或者
数学等式选出第一条记录和适当数量的递增记录。这一操作可以通过好几种方式来完成,但是
Select 语句只显示一种可能(这里的ID 是自动生成的号码):
sql = "Select * FROM Customers Where ID BETWEEN " & RNumber & " AND " & RNumber & "+ 9"
注意:以上代码的执行目的不是检查数据库内是否有9条并发记录。
随机读取若干条记录,测试过
Access语法:
Select top 10 * From 表名 orDER BY Rnd(id) sql server:select top n * from 表名 order by newid() mysqlelect * From 表名 order By rand() Limit n
Access左连接语法(最近开发要用左连接,Access帮助什么都没有,网上没有Access的SQL说明,只有
自己测试, 现在记下以备后查)
语法
select table1.fd1,table1,fd2,table2.fd2 From table1 left join table2 on table1.fd1,table2.fd1 where ...
使用SQL语句 用…代替过长的字符串显示
语法:
SQL数据库:
select case when len(field)>10 then left(field,10)+'...' else field end as news_name,news_id from tablename
Access数据库:
Select iif(len(field)>2,left(field,2)+'...',field) FROM tablename;
Conn.Execute说明
Execute方法
该方法用于执行SQL语句。根据SQL语句执行后是否返回记录集,该方法的使用格式分为以下两
种:
(1).执行SQL查询语句时,将返回查询得到的记录集。用法为:
Set 对象变量名=连接对象.Execute(“SQL 查询语言”)
Execute方法调用后,会自动创建记录集对象,并将查询结果存储在该记录对象中,通过Set
方法,将记录集赋给指定的对象保存,以后对象变量就代表了该记录集对象。
(2).执行SQL的操作性语言时,没有记录集的返回。此时用法为:
连接对象.Execute “SQL 操作性语句” [, RecordAffected][, Option]
?RecordAffected 为可选项,此出可放置一个变量,SQL语句执行后,所生效的记录
数会自动保存到该变量中。通过访问该变量,就可知道SQL语句队多少条记录进行了操作。
?Option 可选项,该参数的取值通常为adCMDText,它用于告诉ADO,应该将Execute
方法之后的第一个字符解释为命令文本。通过指定该参数,可使执行更高效。
*BeginTrans、RollbackTrans、CommitTrans方法
这三个方法是连接对象提供的用于事务处理的方法。BeginTrans用于开始一个事物;
RollbackTrans用于回滚事务;CommitTrans用于提交所有的事务处理结果,即确认事务的处理。
事务处理可以将一组操作视为一个整体,只有全部语句都成功执行后,事务处理才算成功;若
其中有一个语句执行失败,则整个处理就算失败,并恢复到处里前的状态。
BeginTrans和CommitTrans用于标记事务的开始和结束,在这两个之间的语句,就是作为事务
处理的语句。判断事务处理是否成功,可通过连接对象的Error集合来实现,若Error集合的成员个
数不为0,则说明有错误发生,事务处理失败。Error集合中的每一个Error对象,代表一个错误信
息。
37、一道SQL语句面试题,关于group by
表内容:
2005-05-09 胜
2005-05-09 胜
2005-05-09 负
2005-05-09 负
2005-05-10 胜
2005-05-10 负
2005-05-10 负
如果要生成下列结果, 该如何写sql语句?
胜 负
2005-05-09 2 2
2005-05-10 1 2
答:代码如下:
create table #tmp(rq varchar(10),shengfu nchar(1))
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-09′,’胜’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-09′,’胜’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-09′,’负’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-09′,’负’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-10′,’胜’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-10′,’负’)
insert into #tmp values(‘2005-05-10′,’负’)
1)select rq, sum(case when shengfu=’胜’ then 1 else 0 end)’胜’,sum(case when shengfu=’
负’ then 1 else 0 end)’负’ from #tmp group by rq
2) select N.rq,N.勝,M.負 from (
select rq,勝=count(*) from #tmp where shengfu=’胜’group by rq)N inner join
(select rq,負=count(*) from #tmp where shengfu=’负’group by rq)M on N.rq=M.rq
3)select a.col001,a.a1 胜,b.b1 负 from
(select col001,count(col001) a1 from temp1 where col002=’胜’ group by col001) a,
(select col001,count(col001) b1 from temp1 where col002=’负’ group by col001) b
where a.col001=b.col001
38、请教一个面试中遇到的SQL语句的查询问题
表中有A B C三列,用SQL语句实现:当A列大于B列时选择A列否则选择B列,当B列大于C列时选择B列
否则选择C列。
示例如下:
select (case when a>b then a else b end ),
(case when b>c then b esle c end)
from table_name
39、一个日期判断的sql语句?
请取出tb_send表中日期(SendTime字段)为当天的所有记录?(SendTime字段为datetime型,包含日
期与时间)
示例如下:
select * from tb where datediff(dd,SendTime,getdate())=0
40、有一张表,里面有3个字段:语文,数学,英语。其中有3条记录分别表示语文70分,数学80分
,英语58分,请用一条sql语句查询出这三条记录并按以下条件显示出来(并写出您的思路):
大于或等于80表示优秀,大于或等于60表示及格,小于60分表示不及格。
显示格式:
语文 数学 英语
及格 优秀 不及格
示例如下:
select
(case when 语文>=80 then ‘优秀’
when 语文>=60 then ‘及格’
else ‘不及格’) as 语文,
(case when 数学>=80 then ‘优秀’
when 数学>=60 then ‘及格’
else ‘不及格’) as 数学,
(case when 英语>=80 then ‘优秀’
when 英语>=60 then ‘及格’
else ‘不及格’) as 英语,
from table
41、在sqlserver2000中请用sql创建一张用户临时表和系统临时表,里面包含两个字段ID和
IDValues,类型都是int型,并解释下两者的区别?
用户临时表:create table #xx(ID int, IDValues int)
系统临时表:create table ##xx(ID int, IDValues int)
区别:
用户临时表只对创建这个表的用户的Session可见,对其他进程是不可见的.
当创建它的进程消失时这个临时表就自动删除.
全局临时表对整个SQL Server实例都可见,但是所有访问它的Session都消失的时候,它也自动删除.
42、sqlserver2000是一种大型数据库,他的存储容量只受存储介质的限制,请问它是通过什么方
式实现这种无限容量机制的。
它的所有数据都存储在数据文件中(*.dbf),所以只要文件够大,SQL Server的存储容量是可以扩
大的.
SQL Server 2000 数据库有三种类型的文件:
主要数据文件
主要数据文件是数据库的起点,指向数据库中文件的其它部分。每个数据库都有一个主要数据文件
。主要数据文件的推荐文件扩展名是 .mdf。
次要数据文件
次要数据文件包含除主要数据文件外的所有数据文件。有些数据库可能没有次要数据文件,而有些
数据库则有多个次要数据文件。次要数据文件的推荐文件扩展名是 .ndf。
日志文件
日志文件包含恢复数据库所需的所有日志信息。每个数据库必须至少有一个日志文件,但可以不止
一个。日志文件的推荐文件扩展名是 .ldf。
43、请用一个sql语句得出结果
从table1,table2中取出如table3所列格式数据,注意提供的数据及结果不准确,只是作为一个格
式向大家请教。
如使用存储过程也可以。
table1
月份mon 部门dep 业绩yj
一月份 01 10
一月份 02 10
一月份 03 5
二月份 02 8
二月份 04 9
三月份 03 8
table2
部门dep 部门名称dname
——————————–
01 国内业务一部
02 国内业务二部
03 国内业务三部
04 国际业务部
table3 (result)
部门dep 一月份 二月份 三月份
————————————–
01 10 null null
02 10 8 null
03 null 5 8
04 null null 9
——————————————
1)
select a.部门名称dname,b.业绩yj as ‘一月份’,c.业绩yj as ‘二月份’,d.业绩yj as ‘三月份’
from table1 a,table2 b,table2 c,table2 d
where a.部门dep = b.部门dep and b.月份mon = ‘一月份’ and
a.部门dep = c.部门dep and c.月份mon = ‘二月份’ and
a.部门dep = d.部门dep and d.月份mon = ‘三月份’ and
2)
select a.dep,
sum(case when b.mon=1 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘一月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=2 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘二月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=3 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘三月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=4 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘四月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=5 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘五月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=6 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘六月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=7 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘七月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=8 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘八月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=9 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘九月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=10 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘十月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=11 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘十一月份’,
sum(case when b.mon=12 then b.yj else 0 end) as ‘十二月份’,
from table2 a left join table1 b on a.dep=b.dep
44、华为一道面试题
一个表中的Id有多个记录,把所有这个id的记录查出来,并显示有多少条记录。
————————————————-
select id, Count(*) from tb group by id having count(*)>1
select*from(select count(ID) as count from table group by ID)T where T.count>1